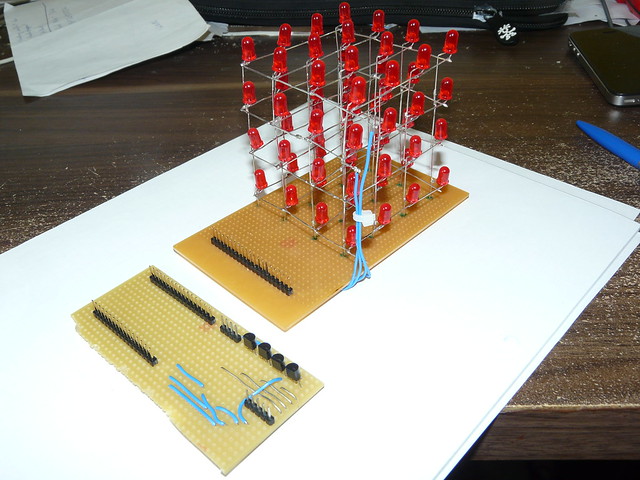
Den LED-Cube werde ich über einen ArduinoMega mit den unten aufgeführten C-Code ansteuern.

ArduinoMega mit ATmega2560 Prozessor
Der ArduinoMega hat folgende Eigenschaften
Microcontroller: ATmega2560
Operating Voltage: 5V
Input Voltage (recommended): 7-12V
Input Voltage (limits): 6-20V
Digital I/O Pins: 54 (of which 15 provide PWM output)
Analog Input Pins: 16
DC Current per I/O Pin: 40 mA
DC Current for 3.3V Pin: 50 mA
Flash Memory: 256 KB of which 8 KB used by bootloader
SRAM: 8 KB
EEPROM: 4 KB
Clock Speed: 16 MHz
Davon nutzen werde ich folgenden Teil:
Ebenen (von unten nach oben, z = 0..3) an Pins A0, A1, A2, A3
LEDs erste Reihe (y = 0) an Pins 22, 23, 24, 25
LEDs zweite Reihe (y = 1) an Pins 26, 27, 28, 29
LEDs dritte Reihe (y = 2) an Pins 30, 31, 32, 33
LEDs letzte Reihe (y = 3) an Pins 34, 35, 36, 37
/*
cube
*/
#define LAYERs 4
#define COLs 4
#define ROWs 4
/* global variable definitions */
unsigned char LEDs[LAYERs][COLs * ROWs];
unsigned char pwmpos = 0; // actual step of the PWM
unsigned char layer = 1; // actual controlled layer
/*
* cmp_carry_shift_left compares the two parameters
* which results in the carry bit to be set/unset
* that carry bit is rotated into para_io
* the complete function consumes only 2 cycles
*/
static inline unsigned char cmp_carry_shift_left (
unsigned char para_io,
unsigned char cmp_para_1,
unsigned char cmp_para_2 )
{
asm volatile (
// compare the parameters
// (get the carry flag set/unset)
"cp %r[cmp2], %r[cmp1]" "\n\t"
// rotate carry bit into paramter
"rol %r[out]" "\n\t"
// output operand
: [out] "+r" (para_io)
// input operands
: [in] "r" (para_io),
[cmp1] "r" (cmp_para_1),
[cmp2] "r" (cmp_para_2)
);
return para_io;
}
/*
* The timer3 overflow interrupt routine builds the pin states
* to be output. the actual output is done in the beginning
* (of the next execution) of the routine to achieve a more
* constant time behaviour
*/
ISR ( SIG_OVERFLOW3 )
{
static unsigned char porta, portc, portf;
PORTB = 0x80; // turn on pin B7 for measuring the time consumption
PORTA = porta; // turn on the pins of PORTA and B in resull of
PORTC = portc; // the previous cycles outcome
PORTF = portf;
pwmpos++;
if ( pwmpos >= 128 ) pwmpos = 0;
if ( pwmpos == 0 )
{
layer++;
if (layer == LAYERs)
{
layer = 0;
PORTB |= 0x10; // get an impulse on Pin B4 as debug output
PORTB &= ~0x10; // -"-
PORTA = 0;
PORTC = 0;
}
portf = 1 <= LAYERs * COLs * ROWs ) ? 0 : RX_pos + 1;
}
PORTB &= ~0x08; // turn off B3 as debug output
}
void setup() {
unsigned char i;
// Initialize port directions and output values
DDRA = 0xFF; PORTA = 0xFF; // first 8 LEDs
DDRC = 0xFF; PORTC = 0xFF; // second 8 LEDs
DDRF = 0x0F; PORTF = 0x01; // 4 layers
DDRB = 0xFF; PORTB = 0x00; // debug output LEDs
// Initialize timer
TCCR3A = (1 << WGM31) | (1 << WGM30) | (0x00 << COM3B0);
TCCR3B = (0x01 << CS30) | (1 << WGM32) | (1 << WGM33);
TIMSK3 |= 1 << TOIE3;
OCR3A = 0xFF; // */
// init LEDs array
for ( i = 0; i < LAYERs * COLs * ROWs; i++ )
( (unsigned char *) LEDs )[i] = 1;
// Enable interrupts
sei();
// listen on RS232 for new data
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void loop() {
PORTB ^= 0x02; // debug output (toggles pin B1 if nothing else is done)
}
Der Programmcode wird ganz simple mit der eigenen Arduino-Applikation via USB auf den Microkontroller in einem Rutsch kompiliert und hochgeladen. Code in das Fenster einfügen und Upload-Button klicken. Fertig!

Programm zum bespielen von Arduino’s